
1.What is Silicone resin?
Silicone resins, also called silicon resins, are used in various fields such as electricity, electronics, automobiles, construction, chemicals, cosmetics, textiles, and foods. Generally, silicone resins are polymers with organic substituents that are made by hydrolyzing silane compounds and increasing their molecular weight through siloxane bonds, and are called hybrid polymers that fuse inorganic and organic elements. Silicone resins exhibit very unique properties due to their structure, and can be customized to meet specific applications by controlling the structure and introducing various organic functional groups. More than 70 years have passed since industrial production began, and the number of patents applied for is increasing year by year, making it a material that is attracting attention and for which further development is expected.
2.Reaction Mechanism
For silicone resins, curing reactions can be selected to suit the conditions of use. Typical curing reactions are shown below.
① Dehydration-condensation reaction between silanol groups
(Si-OH + HO-Si → Si-O-Si + H2O)
This reaction is widely used in curing reactions such as silicone resins. Basically, the curing reaction proceeds by heating, and metallic catalysts are often used.
② Condensation reaction between silanol groups and hydrolyzable groups
(Si-OH + RO-Si → Si-O-Si + R-OH)
This reaction is used in the curing reaction of silicone resins and condensation-type liquid silicone rubber. Basically, the reaction proceeds at room temperature in the presence of acid, alkali, and metal catalysts. Hydrolyzable groups (RO-Si) include alkoxy groups, acetoxy groups, oxime groups, aminoxy groups, and propenoxy groups, which are used depending on the application.
③Addition reaction between vinylsilyl group and hydrosilyl group
(Si-CH=CH2 + H-Si → Si-CH2-CH2-Si)
This reaction is widely used as a curing reaction for silicone rubber, silicone resin, and release paper. Addition reactions can be used for both room temperature curing and heat curing, and can be used for curing in both open and closed systems. Also, unlike condensation reactions, no byproducts are produced in the reaction process, so the cured product has excellent sealing and heat resistance. On the other hand, the use of a platinum catalyst is essential for the reaction, and the curing process is hindered by trace amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur compounds that interfere with the catalytic activity of the catalyst.
3.Features and Strengths
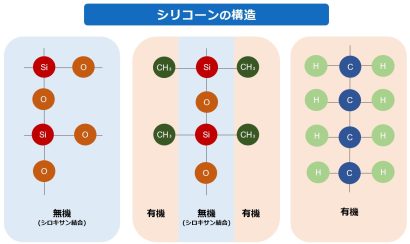
Silicone resin has an inorganic siloxane bond (-Si-O-Si-) in the main chain and organic groups such as methyl and phenyl groups in the side chains, making it a hybrid material with both inorganic and organic properties.
Compared to organic polymers, which are generally composed of C-C bonds in the main chain, silicone resin has a wide variety of properties, including heat resistance, cold resistance, weather resistance, electrical properties, water repellency, and mold release properties.
The basic structure of silicone resin is characterized by its helical structure, with hydrophilic Si-O bonds on the inside and hydrophobic organic groups on the outside.
This helical structure is stabilized by ionic attraction, and because the outside is covered with hydrophobic organic groups, the surface energy and attraction between silicone resins are relatively weak.
As a result, it exhibits unique characteristics not found in other plastic materials, such as defoaming, mold release, water repellency, high compressibility, high gas permeability, good cold resistance, and small temperature dependence of various properties.
4.Use

Silicone resins have a wide variety of features and benefits and are used in diverse applications including construction, electronics/electrical, general industrial, personal/lifestyle, and transportation machinery. Our typical applications include the following
①Heat-resistant sealing materials
These encapsulants take advantage of the heat resistance of silicone resin, which is not found in other organic resins, and have a long track record in the encapsulation of electronic components such as resistors and temperature sensors. We have a lineup of concretes and low-temperature curing types for applications requiring low cost.
➁ Non-combustible coating for exterior installation
This coating takes advantage of the nonflammability and heat resistance of silicone resin. It has a long track record of use in exterior applications for electronic components such as resistors and thermistors.
③Materials for LED
Silicone resins have excellent heat and light resistance, and are used in LEDs for lighting, TV backlights, and other applications requiring long-term reliability. Silicone resins are used in the following applications.
(ⅰ) encapsulating materials,
(ⅱ) die bonding materials,
(ⅲ) reflectors,
(ⅳ) silicone lenses,
(ⅴ) heat dissipation materials.
We have experience with encapsulating materials and die bonding materials.
⑤Mold release agent
The surface of the silicone molecule is covered with methyl groups, which lowers its surface energy and cohesion (the ability of molecules to attract each other).
For example, silicone coated on the surface of a resin molding die spreads thinly over the surface of the mold. If thermoplastic resin is poured into it, it can be easily peeled off even after the resin has cooled.
Because of its chemical inertness, excellent heat and cold resistance, and superior performance over a wide temperature range, silicone is used as a mold release agent in a variety of fields, including the rubber industry, resin industry, food industry, and die casting. Silicone release agents are available in emulsion, oil, solution, baking, and spray types.
We have a long track record in spray type EPOLEASE.

