
1.What is Polyurethane resin?
In a narrow sense, polyurethane resins are compounds with intramolecular urethane bonds, but in a broader sense, they are all resins derived from isocyanate compounds, including urea, biuret, allophanate, carbodiimide, etc. In 1937, Otto Bayer et al. Since the discovery of the practical application of polyurethanes by Otto Bayer et al. in Germany in 1937, polyurethanes have been used in a wide range of applications, from gels to elastomers and even foams used in rigid plastics, insulation, cushioning, and more. This wide range of applications is due to the fact that polyurethane resins can be freely designed through the selection of raw materials, which can be said to be the greatest feature of polyurethane resins.
2.Reaction Mechanism
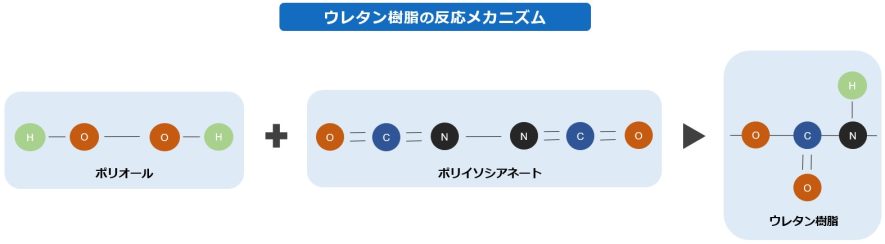
The basic reaction for the formation of a urethane bond is the reaction of an isocyanate group with a hydroxyl group. The nucleophilic oxygen atom of the hydroxyl group reacts with the electrophilic carbon of the isocyanate group to form a urethane bond. Polyurethane resins are obtained through a polyaddition reaction of bifunctional or higher isocyanates and bifunctional or higher polyols using the aforementioned reaction. Polyaddition reactions are characterized by the fact that there are no byproducts and the reaction proceeds quantitatively, making molecular design easy. It is also known that the reactivity of isocyanate and polyol, the raw materials, varies depending on their molecular structures. For example, isocyanates are more reactive in aromatic systems than in aliphatic systems because the resonance structure increases the electrophilicity of the carbon. On the other hand, polyols have higher reactivity in the order of primary > secondary > tertiary alcohols due to steric hindrance. Urethanation reactions usually proceed spontaneously at room temperature without heating or catalysts because of the high reaction rate. Organometallic catalysts such as tin and tertiary amines are used as catalysts.
3.Features and Strengths
Since urethane bonds have strong cohesive energy, intermolecular forces (hydrogen bonds) between urethane bonds, which are hard segments, form localized aggregates called hard domains. This aggregate is called a microphase-separated structure. When this aggregate is strongly formed, crystalline and amorphous portions are mixed in the cured material, and light is refracted and scattered, making it opaque. Intentional formation of a microphase-separated structure increases the number of pseudo cross-linking points derived from hydrogen bonding, resulting in high elongation, toughness, and impact resistance in the room temperature range. Although it is a thermosetting resin, urethane resins are characterized by their ability to impart specific properties through structures other than covalent bonding. Also, by controlling the structure and molecular weight distribution, it is possible to design elastic to buffer bodies, and by selecting molecular chains, heat resistance, water resistance, and even water absorbency.
4.Use

Polyurethane resins are used in a wide variety of applications because they can be given distinctive performance characteristics through the selection of raw materials. For example, they are used as soft and hard foams, elastomers, paints, adhesives, sealants, civil engineering and construction materials, artificial leathers, and sealants in a wide range of fields such as industrial materials, medical materials, and household materials.
①Various electronic components (including automotive)
Flexibility is one of the characteristics of polyurethane resins. Because of their excellent stress relaxation and vibration absorption properties, they are applied to sensors and other components to protect them from all environmental factors. Especially in automotive applications, the demand for low glass transition temperatures and heat resistance has expanded the range of applications for high-performance polyurethane resins.
②Industrial Model/Low Pressure RIM
In the consumer electronics and automotive industries, prototypes are generally made to confirm the shape and design before mass production. Vacuum casting is a method of making prototypes without using expensive molds. In vacuum casting, urethane material is poured under vacuum into a silicone rubber mold based on a master model. The lineup of urethane materials includes ABS, PP, elastomer, and acrylic materials. We have a large share of the domestic and Chinese markets. In addition, low-pressure RIM is used in the prototyping of special large automotive decorative parts such as aero parts, in which fast-curing RIM material is injected into a resin mold made of FRP or epoxy putty for molding. This method is used not only for prototyping, but also for small-lot mass production.
③Elastomer for Shoe Soles/Urethane Gel
“Polyurethane resins are widely used in elastomers and gels because of their flexibility. Urethane elastomers control their physical properties by creating a strong microphase-separation structure. We are using our elastomer compounding technology to expand applications to elastic adhesives and elastic coating materials. For example, MU-697, used in marathon shoes, offers high strength, high elongation, excellent grip, and abrasion resistance.
④Urethane foam
Urethane foam used for insulation, cushioning, etc. may use a solvent-based foaming agent. We are promoting environmentally friendly formulations that do not use solvents and instead use water foaming. It has a proven track record in decorative applications, etc., and features a long cream time (excellent workability).
⑤Non-yellowing material/Transparent material
Doming” is a technique for potting transparent resin on a base material to give a luxurious look to stickers, badges, and other items. Our MU-636 series of urethane materials with excellent weather resistance has a high market share as emblems for automobiles, home appliances, etc. Furthermore, we are using this compounding technology to expand applications to food samples, LEDs, light guide materials, and coating materials.

